Introduction to Innovative Teaching Strategies
Innovative teaching strategies are a wide range of modern pedagogical techniques that aim to enhance the learning experience and academic outcomes for students. These strategies can include various approaches such as technology integration, student-centered learning, interdisciplinary teaching, and creative thinking methods.
In today’s rapidly evolving educational scenario, innovative teaching strategies play a pivotal role in shaping the learning experiences of students. These approaches, characterized by creativity, adaptability, and forward-thinking, are essential for meeting the diverse needs of learners and preparing them for success in a dynamic world. In this blog post, we will explore the concept of innovative teaching strategies, their significance in education, and the diverse range of approaches that educators can employ to enhance student engagement, learning outcomes, and overall educational experience.

Definition of Innovative Teaching Strategies
Innovative teaching strategies refer to unconventional, new, and forward-looking approaches to instruction that go beyond traditional methods to engage, motivate, and empower learners. These strategies leverage emerging technologies, creative pedagogies, and research-based practices to facilitate deeper understanding, critical thinking, and skill development among students. Embracing innovation in teaching, educators can create dynamic learning environments that foster curiosity, creativity, and lifelong learning skills.
Importance of Incorporating Innovative Strategies in Education
Incorporating innovative teaching strategies is essential for addressing the evolving needs of today’s learners and preparing them for the challenges and opportunities of the 21st century. These strategies promote active learning, critical thinking, problem-solving, and collaboration, equipping students with the skills and competencies needed to succeed in a rapidly changing world. Innovative teaching approaches also foster student engagement, motivation, and enjoyment of learning, leading to improved academic performance and overall educational outcomes.
This article Will Cover
Throughout this article, we are going to explore a variety of innovative teaching strategies that educators can implement to enhance the learning experiences of students. We will discuss approaches such as flipped classrooms, project-based learning, gamification, personalized learning, collaborative learning spaces, experiential learning, inquiry-based instruction, blended learning, augmented reality (AR) and virtual reality (VR), and data-driven instruction. Examining the benefits, challenges, and practical implementation strategies of these innovative approaches, readers will gain insights into how they can incorporate innovation into their teaching practices to maximize student engagement, learning, and success.
Understanding Innovative Teaching Strategies
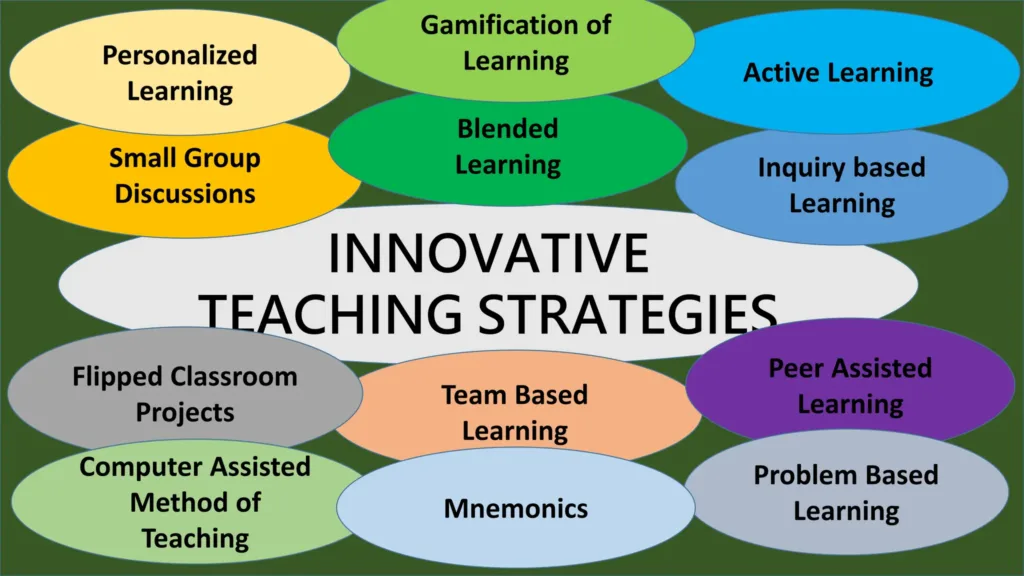
Explanation of Innovative Teaching Methods
Innovative teaching methods include a wide range of approaches that depart from traditional instructional practices to engage students in dynamic and interactive learning experiences. These methods prioritize creativity, flexibility, and adaptability, aiming to meet the diverse needs and learning styles of students in today’s ever-changing educational landscape. Innovative teaching methods often leverage emerging technologies, interdisciplinary approaches, and active learning strategies to promote deeper understanding, critical thinking, and skill development among learners.
Examples of Innovative Strategies in Education
Flipped Classroom
In a flipped classroom model, instructional content is delivered outside of class time through videos, readings, or online modules, allowing students to engage with the material at their own pace. Class time is then used for interactive activities, discussions, and collaborative projects, enabling deeper exploration and application of concepts.
The flipped classroom model represents a paradigm shift in traditional teaching methods, revolutionizing the way educators deliver instruction and engage students in learning. In this innovative approach, instructional content is flipped, with students accessing materials such as videos, readings, or online modules outside of class time. This allows them to engage with the material at their own pace, reviewing concepts, taking notes, and absorbing information according to their individual learning preferences and needs.
Through Flipp Classroom, educators can maximize the value of face-to-face instructional time, transforming it into a dynamic and interactive learning environment. Class time becomes a space for active engagement, meaningful discussions, and collaborative projects, where students have the opportunity to delve deeper into concepts, ask questions, and apply their knowledge in real-world contexts.
The flipped classroom model is the ability to promote student-centered learning and autonomy. With access to instructional materials outside of class, students have greater control over their learning journey, allowing them to take ownership of their education and develop self-regulated learning skills. They can pause, rewind, and review content int as needed, ensuring comprehension and mastery of concepts before engaging in-class activities.
Moreover, the flipped classroom fosters a collaborative and interactive learning community where students actively participate in their learning process. Class time is utilized for hands-on activities, group discussions, and peer collaboration, enabling students to learn from each other, share ideas, and work together to solve problems. This promotes critical thinking, communication skills, and teamwork, essential competencies for success in the 21st century.
The flipped classroom model has been shown to improve learning outcomes. Research indicates that students in flipped classrooms demonstrate increased retention of material, and a deeper understanding of concepts, and higher levels of academic achievement compared to traditional instructional methods. By providing more opportunities for active learning and application of knowledge, the flipped classroom empowers students to achieve academic success and develop lifelong learning skills.
However, implementing the flipped classroom model comes with its own set of challenges and considerations. Educators must carefully plan and design instructional materials to ensure they are engaging, accessible, and aligned with learning objectives. They must also provide support and guidance to students as they navigate the flipped learning environment, addressing any questions or concerns that may arise.
Despite these challenges, the flipped classroom offers a transformative approach to teaching and learning, empowering educators to create dynamic, student-centered learning experiences that foster curiosity, creativity, and collaboration. By embracing the flipped classroom model, educators can harness the power of technology and pedagogy to unlock the full potential of every student, preparing them for success in an ever-changing world.
Project-Based Learning (PBL)
Project-based learning is a powerful educational approach that promotes student-centered, inquiry-based, and experiential learning. Engaging students in extended, interdisciplinary projects that address real-world challenges, PBL cultivates critical thinking, collaboration, and problem-solving skills while fostering a lifelong love of learning. As educators continue to explore innovative teaching methods, project-based learning stands out as a transformative approach that prepares students for success in the 21st century and beyond
Project-based learning involves students working on extended, interdisciplinary projects that address real-world challenges or problems. Through inquiry, collaboration, and hands-on experiences, students develop critical thinking, problem-solving, and communication skills while applying content knowledge in authentic contexts.
Project-Based Learning (PBL) represents a dynamic approach to education that shifts the focus from passive learning to active learning and engagement, empowering students to become critical thinkers, problem solvers, and lifelong learners. At its core, PBL involves students working on extended, interdisciplinary projects that center around real-world challenges or problems. Unlike traditional teaching methods that prioritize memorization and rote learning, PBL emphasizes inquiry, collaboration, and hands-on experiences, enabling students to apply their content knowledge in authentic contexts and develop essential 21st-century skills.
In a project-based learning environment, students are tasked with identifying, investigating, and addressing complex problems or questions that are relevant to their lives and communities. This often involves conducting research, gathering data, and analyzing information from multiple sources to gain a deeper understanding of the topic at hand. By engaging in inquiry-based learning, students develop critical thinking skills as they evaluate evidence, draw connections, and make informed decisions to solve real-world problems.
Project-based learning emphasizes collaboration and teamwork, mirroring the collaborative nature of the professional world. Students work together in groups or teams, leveraging their strengths and perspectives to tackle complex challenges and achieve shared goals. Through collaboration, students learn how to communicate effectively, resolve conflicts, and collaborate with others to achieve common objectives, essential skills for success in any field or career.
Hands-on experiences are essential to the fundamental aspect of project-based learning, allowing students to apply theoretical knowledge in practical, real-world contexts. Whether conducting experiments, designing prototypes, or creating multimedia presentations, students actively engage in the learning process and develop skills that are transferable to diverse settings and situations. Participating in hands-on activities, students not only deepen their understanding of concepts but also gain valuable experience in problem-solving, creativity, and innovation.
The key strength of project-based learning is its ability to foster intrinsic motivation and a love of learning. Giving students autonomy and agency over their projects, PBL empowers them to take ownership of their learning and pursue topics that are meaningful and relevant to their interests and passions. This intrinsic motivation drives students to invest time and effort into their projects, leading to deeper engagement, higher levels of achievement, and a sense of accomplishment.
Gamification
Gamification integrates game elements such as points, badges, and leaderboards into educational activities to motivate and engage students. By turning these learning tasks into interactive games, educators can increase student motivation, promote healthy competition, and foster a sense of achievement and progress.
Gamification represents a dynamic approach to education that harnesses the power of game design principles to enhance student engagement, motivation, and learning outcomes. Gamification integrates elements such as points, badges, leaderboards, and rewards into educational activities, transforming learning tasks into interactive games that captivate and inspire students.
Infusing educational activities with game elements, educators can tap into intrinsic motivators such as competition, achievement, and mastery, driving students to actively participate and excel in their learning journey. Points, badges, and leaderboards serve as tangible indicators of progress and accomplishment, providing students with a sense of achievement and recognition for their efforts.
Gamification is its ability to increase student motivation and engagement. Leveraging game mechanics such as challenges, quests, and rewards, educators create immersive learning experiences that capture students’ attention and inspire them to invest time and effort into their academic pursuits. Gamified activities tap into students’ natural desire for challenge and accomplishment, encouraging them to overcome obstacles, push their limits, and strive for excellence.
Gamification promotes healthy competition among students, fostering a sense of camaraderie and collaboration as they compete for high scores, earn badges, and climb leaderboards. Competitive elements motivate students to actively participate, challenge themselves, and strive for continuous improvement, driving higher levels of engagement and achievement.
Along with enhancing motivation and engagement, gamification facilitates personalized learning experiences tailored to individual student preferences and abilities. By allowing students to earn points, unlock achievements, and progress at their own pace, educators can cater to diverse learning styles and interests, ensuring that each student feels challenged and supported in their learning journey.
Gamification promotes active learning and skill development by encouraging students to apply their knowledge and problem-solving abilities in interactive, game-based scenarios. Whether solving puzzles, completing quests, or participating in simulations, students engage in hands-on activities that reinforce learning objectives and promote critical thinking, creativity, and collaboration.
Gamification offers a transformative approach to education that empowers educators to create dynamic, engaging, and personalized learning experiences. By integrating game elements into educational activities, educators can increase student motivation, promote healthy competition, and foster a sense of achievement and progress. As educators continue to explore innovative teaching methods, gamification stands out as a powerful tool for inspiring students to excel academically and develop essential 21st-century skills.
Personalized Learning
Personalized learning is an instruction strategy to meet the individual needs, interests, and learning styles of each student. Through adaptive technologies, differentiated instruction, and flexible pacing, educators provide personalized learning pathways that allow students to progress at their own pace and receive targeted support and feedback.
Personalized learning stands as a key factor in modern education, aiming to address the unique needs, preferences, and learning styles of individual students. Personalized learning involves such type of instruction strategy that accommodates the diverse needs and interests of each learner, fostering an environment where every student can thrive and succeed.
This approach to education leverages various strategies and tools, including adaptive technologies, differentiated instruction, and flexible pacing, to create personalized learning ways for students. Adaptive technologies, such as educational software and online platforms, analyze student data and provide customized learning experiences that adapt to each student’s strengths, weaknesses, and progress. These technologies offer interactive exercises, quizzes, and assessments that adjust difficulty levels based on individual performance, ensuring that students receive targeted support and challenges as needed.
Differentiated instruction plays a pivotal role in personalized learning by offering multiple pathways for students to access and engage with content. Educators modify their teaching methods, materials, and assessments to accommodate diverse learning styles, preferences, and readiness levels. This may involve providing alternative instructional resources, offering choice-based assignments, or implementing tiered activities that allow students to work at their own pace and level of challenge.
Flexible pacing is another hallmark of personalized learning, allowing students to progress through content at a pace that suits their individual needs and abilities. Instead of adhering to rigid timelines and schedules, educators provide opportunities for students to self-pace their learning, allowing them to delve deeper into topics of interest, revisit challenging concepts, or accelerate their progress through mastery-based learning models.
The benefits of personalized learning are many such as encompassing improved academic outcomes, increased student engagement, and enhanced motivation and confidence. Catering to each student’s unique strengths, interests, and learning preferences, personalized learning fosters a sense of ownership and autonomy in the learning process, empowering students to take control of their education and become active participants in their own learning journey.
Personalized learning promotes equity and inclusivity by recognizing and valuing the diverse backgrounds, experiences, and abilities of all students. Providing personalized support and accommodations, educators can address individual learning barriers and ensure that every student has access to high-quality education and opportunities for success.
Personalized learning represents a transformative approach to education that prioritizes the individual needs and aspirations of each student. By embracing adaptive technologies, differentiated instruction, and flexible pacing, educators can create personalized learning experiences that empower students to reach their full potential and become lifelong learners who are equipped to thrive in a rapidly evolving world. As educators continue to innovate and adapt their teaching practices, personalized learning stands as a beacon of progress and possibility in the pursuit of educational excellence and equity for all.
Collaborative Learning Spaces
Collaborative learning spaces are physical or virtual environments designed to facilitate group work, discussions, and cooperative learning activities. Equipped with flexible seating arrangements, interactive whiteboards, and digital tools, these spaces promote communication, collaboration, and knowledge sharing among students.
Collaborative learning spaces play a key role in modern education providing environments where students can collaborate, communicate, and learn from one another in both physical and virtual settings. Equipped with flexible seating arrangements, interactive technologies, and digital tools, these spaces foster collaboration, creativity, and knowledge sharing, ultimately enhancing the overall learning experience for students.
Collaborative learning spaces refer to designated areas, whether physical or virtual, intentionally crafted to encourage group collaboration, discussions, and cooperative learning endeavors among students. These spaces are characterized by their flexible seating arrangements, interactive whiteboards, and integration of digital tools, all of which are geared towards fostering communication, collaboration, and the exchange of knowledge among students.
Collaborative learning spaces serve as hubs where students can come together to engage in collaborative activities, share ideas, and work collectively on academic tasks. These spaces are designed to promote interaction and teamwork, allowing students to collaborate effectively and learn from one another’s perspectives and experiences.
Physical collaborative learning spaces often feature flexible furniture arrangements that can be easily reconfigured to accommodate various group sizes and learning activities. Comfortable seating options, such as bean bags or movable chairs, create a relaxed and inviting atmosphere conducive to open communication and idea exchange. Interactive whiteboards or writable surfaces provide students with opportunities to brainstorm, illustrate concepts, and collaborate on shared projects in real time.
Similarly, virtual collaborative learning spaces leverage digital tools and platforms to facilitate group collaboration and communication in an online environment. These platforms may include video conferencing tools, collaborative document editors, and virtual meeting spaces where students can connect, interact, and collaborate remotely. Through these virtual spaces, students can engage in synchronous or asynchronous discussions, share resources, and collaborate on projects regardless of their physical location.
The primary goal of collaborative learning spaces is to promote active engagement, peer interaction, and deeper learning among students. By providing opportunities for students to collaborate, communicate, and problem-solve together, these spaces encourage the development of critical thinking skills, communication skills, and teamwork abilities essential for success in academic and professional settings.
Experiential Learning
Experiential learning immerses students in hands-on, real-world experiences that allow them to apply theoretical knowledge in practical contexts. Activities such as field trips, internships, simulations, and service-learning projects foster deeper understanding, skill development, and meaningful connections between theory and practice.
Experiential learning plays a vital role in education by providing students with opportunities to engage actively with course material, develop practical skills, and make meaningful connections between theory and practice. By immersing students in hands-on, real-world experiences, experiential learning fosters deeper understanding, skill development, and personal growth, ultimately preparing students for success in both academic and professional settings.
Experiential learning is an educational approach that emphasizes hands-on, real-world experiences as a primary means of learning. Unlike traditional classroom instruction, which often focuses on theoretical concepts and abstract ideas, experiential learning immerses students in practical, tangible experiences where they can apply theoretical knowledge in authentic contexts.
At the heart of experiential learning are activities that engage students in direct, hands-on experiences that are relevant to their academic studies and future career goals. These activities can take various forms, including field trips, internships, simulations, and service-learning projects, among others. Through these experiences, students have the opportunity to engage actively with course content, develop practical skills, and make meaningful connections between theory and practice.
Field trips, for example, provide students with the chance to explore real-world environments related to their academic studies, such as museums, laboratories, or historical sites. By experiencing these environments firsthand, students can deepen their understanding of course concepts and gain valuable insights that may not be possible through classroom instruction alone.
Internships offer students the opportunity to apply classroom knowledge in professional settings, gaining practical experience and developing relevant skills in their chosen field. By working alongside professionals in their field of study, students can gain valuable insights into industry practices, build professional networks, and explore potential career paths.
Simulations, on the other hand, provide students with immersive, interactive experiences that simulate real-world scenarios or processes. Whether conducting a virtual science experiment, participating in a business simulation, or role-playing historical events, students engage in active learning experiences that challenge them to apply theoretical knowledge in practical contexts.
Service-learning projects combine academic coursework with community service, allowing students to address real-world issues while gaining valuable hands-on experience. By partnering with local organizations or community groups, students can apply their knowledge and skills to make a positive impact in their communities while deepening their understanding of course content.
Benefits of Utilizing Innovative Teaching Approaches

Increased Student Engagement: Innovative teaching approaches capture students’ interest and enthusiasm, leading to higher levels of engagement and participation in learning activities.
Enhanced Learning Outcomes: By promoting active learning, critical thinking, and problem-solving, innovative teaching methods contribute to improved academic performance and a deeper understanding of content.
Development of 21st-Century Skills: Innovative teaching approaches equip students with essential skills such as collaboration, communication, creativity, and adaptability, preparing them for success in the modern workforce.
Personalized Learning Experiences: Through personalized instruction and flexible learning pathways, innovative teaching methods cater to the individual needs and learning styles of students, promoting greater autonomy and ownership of learning.
Integration of Technology: Many innovative teaching approaches leverage technology to enhance instruction, facilitate interactive learning experiences, and provide access to a wealth of educational resources and tools.
Promotion of Lifelong Learning: By fostering curiosity, creativity, and a growth mindset, innovative teaching approaches instill a love of learning and empower students to become lifelong learners and critical thinkers.
Understanding innovative teaching strategies involves recognizing their diverse approaches, including flipped classrooms, project-based learning, gamification, personalized learning, collaborative learning spaces, and experiential learning. These strategies offer numerous benefits, including increased student engagement, enhanced learning outcomes, development of 21st-century skills, personalized learning experiences, integration of technology, and promotion of lifelong learning. By embracing innovation in education, educators can create dynamic and inclusive learning environments that empower students to thrive in the digital age.
Types of Innovative Teaching Strategies
Different Categories of Innovative Teaching Techniques:
- Active Learning Strategies:
- Technology Integration:
- Differentiated Instruction:
- Inquiry-Based Learning:
- Collaborative Learning Techniques:
- Flipped Classroom Model
Description of Each Type with Practical Examples
Active Learning Strategies:
Active learning strategies involve student-centered approaches that encourage learners to actively engage with course material through hands-on activities, discussions, and problem-solving exercises. Examples include:
Think-Pair-Share
Students individually reflect on a question or prompt, discuss their thoughts with a partner, and then share their ideas with the class.
Peer Instruction
Students engage in peer-led discussions and collaborative problem-solving activities to deepen understanding of complex concepts.
Case-Based Learning
Students analyze real-life case studies or scenarios to apply theoretical knowledge in practical contexts and develop critical thinking skills.
Technology Integration
Technology integration involves incorporating digital tools, resources, and platforms into teaching and learning activities to enhance engagement, accessibility, and interactivity. Examples include:
Interactive Whiteboards
Teachers use interactive whiteboards to deliver multimedia-rich lessons, annotate content, and engage students in interactive activities.
Educational Apps and Games
Students use educational apps and games to reinforce learning concepts, practice skills, and receive immediate feedback in a fun and engaging manner.
Virtual Field Trips
Students explore virtual environments, museums, and landmarks using virtual reality (VR) or augmented reality (AR) technology to enhance experiential learning and global awareness.
Tiered Assignments
Teachers offer different levels of assignments or tasks based on students’ readiness levels, allowing each student to work at their own pace and challenge themselves appropriately.
Learning Stations
Students rotate through different learning stations or activities that target various learning modalities, allowing them to engage with content in multiple ways and receive personalized instruction.
Flexible Grouping
Teachers group students based on their strengths, interests, or learning needs to facilitate peer collaboration, cooperative learning, and differentiated instruction..
Step-by-Step Guide on Integrating Innovative Methods into Teaching
- Identify Learning Objectives: Begin by clarifying the learning objectives and desired outcomes for the lesson or unit. Determine what knowledge, skills, and competencies you want students to acquire through the use of innovative teaching strategies.
- Select Appropriate Strategies: Choose innovative teaching strategies that align with the learning objectives, student needs, and instructional context. Consider factors such as class size, available resources, and students’ prior knowledge and interests.
- Plan Engaging Activities: Design engaging and interactive learning activities that incorporate the selected innovative teaching strategies. Consider how you will introduce the activity, facilitate student participation, and assess learning outcomes.
- Integrate Technology: Incorporate technology tools and resources to enhance teaching and learning experiences. Explore digital platforms, multimedia resources, and interactive simulations that support the selected teaching strategies and engage students in meaningful ways.
- Provide Clear Instructions: Clearly communicate the purpose, expectations, and guidelines for the activities to students. Provide step-by-step instructions, demonstrations, and examples to ensure that students understand what is expected of them and how to successfully complete the tasks.
- Facilitate Active Learning: Actively engage students in the learning process through collaborative discussions, problem-solving activities, and hands-on experiences. Encourage participation, ask probing questions, and provide opportunities for students to reflect on their learning.
- Foster Collaboration: Promote peer collaboration and teamwork by incorporating group work, cooperative learning activities, and peer feedback into the instructional design. Encourage students to share ideas, collaborate on projects, and learn from each other’s perspectives.
- Monitor Progress and Provide Feedback: Monitor students’ progress throughout the lesson or activity and provide timely feedback to support their learning. Offer constructive feedback, praise student contributions, and address misconceptions or areas of confusion as needed.
- Reflect and Adapt: Reflect on the effectiveness of the innovative teaching strategies used and consider how they can be refined or adapted for future use. Solicit feedback from students, colleagues, and other stakeholders to identify areas for improvement and innovation.
Challenges and Solutions in Implementing Innovative Strategies
Resistance to Change: Some educators may resist implementing innovative teaching strategies due to fear of change or lack of familiarity with new approaches. To address this challenge, provide professional development opportunities, training workshops, and ongoing support to help educators build confidence and develop proficiency in using innovative methods.
Access to Resources: Limited access to technology, instructional materials, and professional development opportunities may pose challenges in implementing innovative teaching strategies. Seek out alternative resources, leverage existing technology infrastructure, and collaborate with colleagues and community partners to overcome resource constraints and access barriers.
Time Constraints: Educators may face time constraints in planning, implementing, and assessing innovative teaching strategies within the constraints of the curriculum and academic schedule. To address this challenge, prioritize essential learning objectives, streamline instructional design processes, and integrate innovative methods into existing lesson plans and activities.
Student Resistance: Some students may be resistant to engaging in new or unfamiliar teaching methods, especially if they are accustomed to traditional instructional approaches. To overcome student resistance, communicate the relevance and benefits of innovative strategies, provide opportunities for student voice and choice, and scaffold learning experiences to support student success and motivation.
Real-Life Case Studies Demonstrating Successful Implementation
Flipped Classroom Model: A high school science teacher implements the flipped classroom model by creating pre-recorded video lectures for students to watch at home, freeing up class time for hands-on experiments, group discussions, and problem-solving activities. As a result, student engagement and understanding of complex scientific concepts improve, leading to higher achievement levels and deeper learning outcomes.
Project-Based Learning (PBL): A middle school social studies teacher designs a project-based learning unit on ancient civilizations, where students work in small groups to research, design, and present their own museum exhibits. Through collaborative inquiry, critical thinking, and creative expression, students develop a deeper understanding of historical events and cultures, while also honing presentation skills and teamwork abilities.
Technology Integration: An elementary school teacher integrates technology tools such as educational apps, interactive whiteboards, and virtual field trips into daily instruction to enhance student engagement and learning. By incorporating digital resources and multimedia content, students develop digital literacy skills, explore new concepts in interactive ways, and access a diverse range of learning materials tailored to their interests and learning styles.
These real-life case studies demonstrate how innovative teaching strategies can be successfully implemented to enhance student engagement, promote deeper learning, and achieve positive outcomes in diverse educational settings. By following a step-by-step approach, addressing common challenges, and drawing on real-world examples, educators can effectively integrate innovative methods into their teaching practices to meet the evolving needs of 21st-century learners.
Assessing the Effectiveness of Innovative Teaching Strategies
Methods for Evaluating the Impact of Innovative Approaches on Student Learning:
Formative Assessment: Use formative assessment techniques such as quizzes, polls, exit tickets, and classroom discussions to gather ongoing feedback on student learning progress and comprehension. Formative assessment provides valuable insights into students’ understanding, identifies areas of confusion, and informs instructional adjustments in real time.
Student Surveys and Feedback: Administer surveys, questionnaires, or feedback forms to students to gather their perspectives on the effectiveness of innovative teaching strategies. Solicit feedback on aspects such as engagement, clarity of instruction, relevance of activities, and overall learning experience to gain insights into students’ perceptions and preferences.
Classroom Observations: Conduct classroom observations or peer evaluations to assess the implementation of innovative teaching strategies and their impact on student engagement, participation, and learning outcomes. Observe student interactions, behaviors, and levels of involvement during instructional activities to identify strengths and areas for improvement.
Learning Analytics: Utilize learning analytics tools and platforms to track student progress, performance, and engagement metrics in digital learning environments. Analyze data such as quiz scores, completion rates, time spent on tasks, and participation levels to assess the effectiveness of innovative teaching strategies and identify patterns or trends in student learning behaviors.
Performance Assessments: Design performance-based assessments, projects, or portfolios that allow students to demonstrate their mastery of learning objectives and competencies. Assess student work using rubrics or criteria aligned with learning goals to evaluate the quality, depth, and creativity of student responses and artifacts.
Importance of Continuous Assessment and Adjustment
Continuous assessment and adjustment are essential for ensuring the effectiveness and relevance of innovative teaching strategies in meeting the evolving needs of students. By continuously monitoring student progress, collecting feedback, and analyzing data, educators can:
Identify Strengths and Areas for Improvement: Continuous assessment helps educators identify effective instructional practices and areas that may require further refinement or adjustment to better support student learning.
Tailor Instruction to Individual Needs: By gathering ongoing feedback on student performance and understanding, educators can tailor instruction to meet the diverse needs, interests, and learning styles of individual students.
Address Challenges and Barriers: Continuous assessment allows educators to identify and address challenges, barriers, or misconceptions that may impede student learning progress and success.
Foster Continuous Improvement: By reflecting on assessment data and feedback, educators can iteratively refine and enhance their teaching practices, instructional materials, and learning experiences to promote continuous improvement and innovation.
Tools and Resources for Measuring Effectiveness
Learning Management Systems (LMS): LMS platforms such as Canvas, Moodle, or Google Classroom provide tools for tracking student progress, administering assessments, and analyzing learning analytics data.
Classroom Response Systems: Classroom response systems like Kahoot, Poll Everywhere, or Socrative enable educators to gather real-time feedback from students through interactive polls, quizzes, or surveys.
Digital Assessment Tools: Digital assessment tools such as Quizizz, Edpuzzle, or Flipgrid offer interactive features for creating and administering formative assessments, performance tasks, or multimedia assignments.
Rubrics and Assessment Guides: Rubrics and assessment guides provide clear criteria and standards for evaluating student work and providing feedback on learning outcomes, performance tasks, or project-based assessments.
Professional Learning Communities (PLCs): Collaborate with colleagues, participate in professional learning communities, or attend workshops and conferences to share best practices, learn from peers, and access resources and support for assessing the effectiveness of innovative teaching strategies.
Leveraging these methods for evaluating the impact of innovative teaching strategies, prioritizing continuous assessment and adjustment, and utilizing tools and resources for measuring effectiveness, educators can ensure that their instructional practices are aligned with student needs, promote meaningful learning experiences, and foster continuous improvement and innovation in education.
Recommendations for educators to enhance their use of innovative strategies.
Recommendations for Educators to Enhance Their Use of Innovative Strategies
Start Small: Begin by incorporating one or two innovative teaching strategies into your lessons or units, and gradually expand your repertoire as you become more comfortable and proficient with implementation.
Seek Professional Development: Attend workshops, conferences, or professional development sessions focused on innovative teaching practices to learn new techniques, gain inspiration, and collaborate with peers.
Collaborate with Colleagues: Share ideas, resources, and best practices with colleagues through professional learning communities, department meetings, or collaborative planning sessions to support each other in implementing innovative strategies.
Reflect and Iterate: Regularly reflect on your teaching practices, gather feedback from students and colleagues, and make adjustments as needed to improve the effectiveness of innovative strategies and enhance student learning outcomes.
Embrace Flexibility: Be open to experimenting with different approaches, adapting instructional methods based on student needs, and adjusting your teaching strategies to meet changing educational contexts and demands.
Advice on Fostering a Supportive Learning Environment
Cultivate a Growth Mindset: Encourage students to embrace challenges, learn from failures, and persist in the face of obstacles by fostering a growth mindset and promoting a positive learning culture.
Establish Clear Expectations: Communicate clear learning objectives, expectations, and guidelines to students, and provide opportunities for them to take ownership of their learning and set goals for growth and improvement.
Foster Collaboration and Community: Create a supportive and inclusive learning environment where students feel valued, respected, and connected to their peers and educators. Encourage collaboration, teamwork, and peer support to promote a sense of belonging and community.
Provide Constructive Feedback: Offer timely and specific feedback to students on their progress, achievements, and areas for improvement, and encourage them to reflect on their learning and set goals for growth and development.
Promote Student Agency: Empower students to take ownership of their learning by providing opportunities for choice, autonomy, and self-directed inquiry. Encourage students to explore their interests, pursue passions, and contribute to their own learning journey.
Tips for Staying Updated with the Latest Trends and Research
Engage in Lifelong Learning: Stay curious, proactive, and engaged in ongoing professional development by seeking out opportunities to learn, grow, and expand your knowledge and skills in innovative teaching practices.
Follow Education Blogs and Journals: Subscribe to education blogs, journals, and publications to stay informed about the latest trends, research findings, and best practices in innovative teaching and learning.
Participate in Online Communities: Join online forums, social media groups, or virtual communities dedicated to education and innovation to connect with educators, share ideas, and exchange resources and insights.
Attend Conferences and Webinars: Participate in conferences, webinars, and virtual events focused on innovative teaching strategies, technology integration, and educational research to stay updated on emerging trends and practices.
Collaborate with Experts: Collaborate with experts in the field of education, instructional design, or technology integration to access specialized knowledge, receive guidance, and gain new perspectives on innovative teaching approaches.
Following these recommendations for enhancing the use of innovative strategies, fostering a supportive learning environment, and staying updated with the latest trends and research, educators can create dynamic, engaging, and impactful learning experiences that inspire curiosity, promote collaboration, and empower students to succeed in the 21st century.
Summary of the Article
In this comprehensive post, we have explored the concept of innovative teaching strategies and their importance in education. We began by understanding innovative teaching methods, examining examples of innovative strategies in education, and highlighting the benefits of utilizing these approaches to enhance student engagement and learning outcomes.
We then explored the different categories of innovative teaching techniques, providing descriptions and practical examples of each type, along with insights into how they contribute to student engagement and learning outcomes. From active learning strategies to technology integration and collaborative learning techniques, educators have a wide array of innovative approaches to choose from to meet the diverse needs of learners.
We discussed the process of implementing innovative teaching strategies, offering a step-by-step guide, addressing challenges, and showcasing real-life case studies demonstrating successful implementation. By following best practices, fostering a supportive learning environment, and staying updated with the latest trends and research, educators can effectively integrate innovative methods into their teaching practices to promote meaningful learning experiences and student success.
The significance of innovation in education cannot be overstated. As we navigate an ever-changing educational landscape, educators must embrace innovation, adapt to new challenges, and explore creative solutions to meet the evolving needs of students. By adopting innovative teaching strategies, educators can create dynamic, engaging, and inclusive learning environments that empower students to thrive academically, socially, and emotionally.
Therefore, I encourage educators to explore, experiment, and adopt innovative teaching strategies in their classrooms. Let us embrace the power of innovation to inspire curiosity, foster creativity, and cultivate lifelong learners who are equipped to navigate the complexities of the 21st century and beyond. Together, we can transform education and empower the next generation of learners to reach their full potential.
Sources
- Third Space Learning – 13 Most Effective Teaching Strategies For School Teachers
- Kaltura – Innovative Teaching Strategies You Must Discover In 2023
- Education Advanced – Innovative Teaching Strategies: Nine Techniques for Success
- Top Hat – 25 Effective Instructional Strategies For Educators
- BookWidgets – 20 interactive teaching activities for in the interactive classroom
- Strobel Education – Unlocking The Benefits Of Innovative Teaching Strategies






[…] to gauge understanding of concepts across the class. This information enables them to adapt their teaching strategies and materials to meet the diverse needs of their students. Lastly, assessments help compare student […]
[…] students to take ownership of their learning and actively participate in the educational process. Teaching self-regulation involves providing students the tools and strategies to manage their thoughts, emotions, and behaviors to achieve academic […]
[…] into educational contexts, educators can create more inclusive, engaging, and effective learning experiences that prepare students for success in a rapidly changing […]
[…] also allows students to learn from each other and build community in the classroom. Peer assessment aims to assess knowledge, […]
[…] These components provide the bedrock for a well-functioning classroom where students can thrive and learn. […]
[…] a positive classroom culture that maximizes instructional time, minimizes disruptions, and enhances student […]
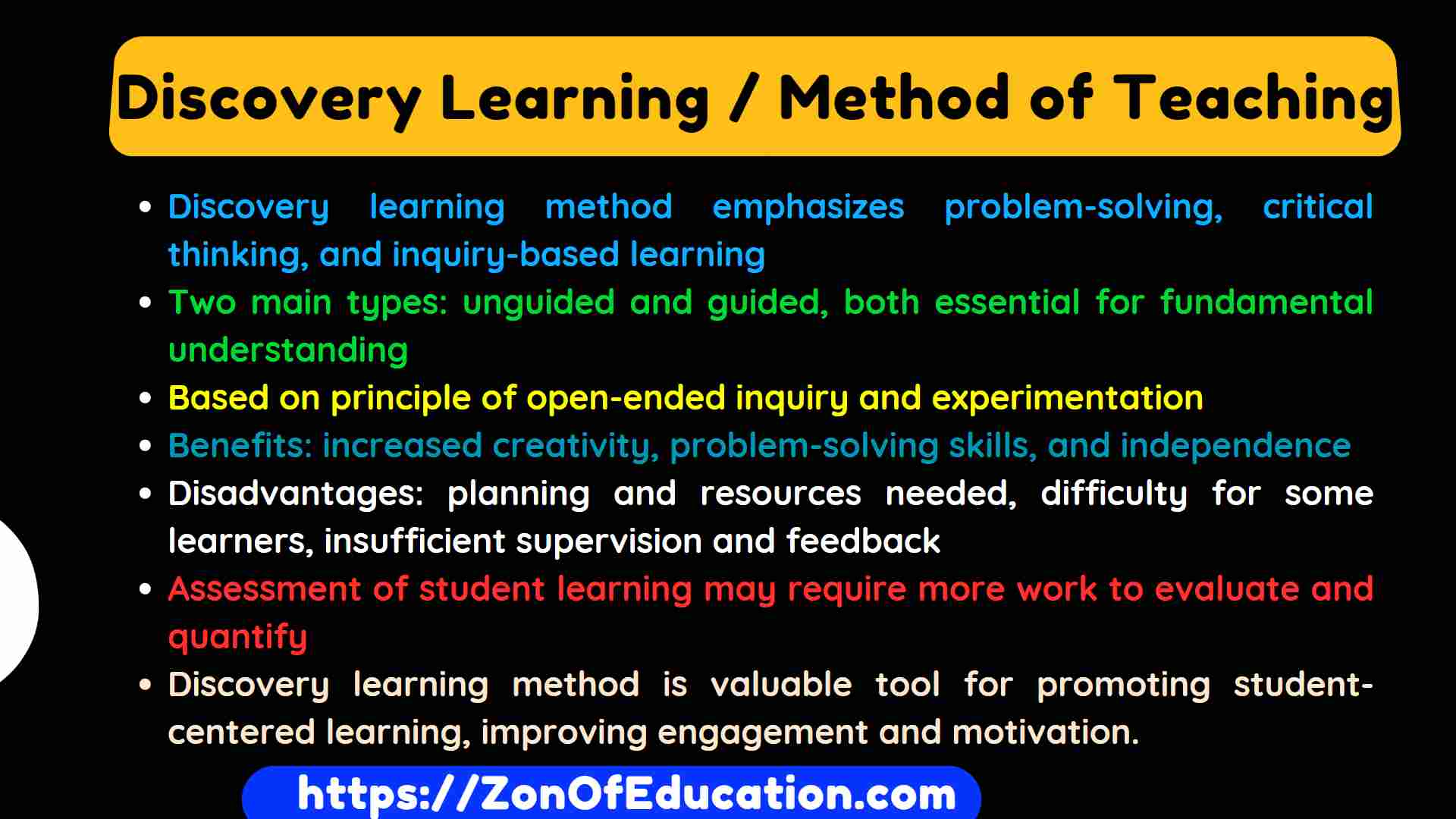
[…] heuristic teaching method is based on the idea that students learn best when actively participating in the learning process. It departs from traditional […]
[…] Learning is a student-centred teaching and learning strategy that promotes problem-solving, critical thinking, and discovery. Students actively participate in […]
[…] methods aim to teach basic ideas and skills in a structured and organized way. Essentialist teaching tries to ensure that all students learn a core set of skills and knowledge, no matter where they come from or what they […]
[…] people a rational way to understand the world and helps them learn how to think critically. Science teaches students to question what they think they know and gives them a more nuanced view of the […]
[…] learn to think independently and critically. Being flexible and willing to modify their teaching strategies to suit the needs of specific students is another requirement of learner-centred […]
[…] intellectual and moral capacities. They are in charge of creating an environment that promotes learning and growth and assisting students in developing a deep appreciation for the pursuit of knowledge and wisdom.The liberal arts, such as […]
[…] is a philosophy that emphasizes the importance of teaching the basic skills and knowledge necessary for students to become productive members of society. It is teacher-centered, and the focus is on developing a […]
[…] students understand the value of their learning, they are more motivated to learn. For example, if students understand the value of learning math, […]
[…] mindset, and character strengths, are integrated into educational interventions and practices to enhance student well-being and academic […]
[…] psychology, educators can gain a deeper understanding of the psychological processes that underlie teaching and learning. Armed with this knowledge, educators can develop effective instructional strategies, create […]
[…] Limited student autonomy: Students have minimal opportunities to make choices or participate actively in th…. […]
[…] principles of educational psychology offer valuable insights and strategies for enhancing teaching practices and promoting student learning in the classroom. Applying these principles effectively, teachers can create engaging, supportive, […]
[…] and responsive to the needs of the individual and society, often incorporating project-based learning and opportunities for student […]
[…] Creativity: Discovery Learning stimulates creativity and innovation by encouraging students to think outside the box and explore unconventional solutions to problems. Through open-ended […]
[…] of them as temperature checks – they provide feedback that allows educators to adjust their teaching strategies to meet individual needs before the final “exam” (summative assessment). Examples […]
[…] plays a crucial role in fostering active participation and enthusiasm among students. Implementing innovative instructional strategies, leveraging technology, and tapping into students’ interests and passions, educators can […]
[…] activities and problem-solving in the real world. This strategy enables students to recognise the practical applications of what they are learning and to build problem-solving abilities applicable in a […]
[…] type of assessment provides actionable suggestions for improvement and allows for adjustments in teaching strategies to meet individual student needs […]
[…] some students may hold traditional views of language learning, expecting a focus on grammar and vocabulary. They may resist the communicative approach or feel […]
[…] distinct characteristics make the demonstration teaching method an effective instructional strategy. Let’s examine some of these key […]
[…] questions into assessments, educators can improve the overall quality of instruction, tailor their teaching strategies to individual student needs, and ensure that learning objectives are […]
[…] assessment is essential for promoting collaborative learning and enhancing students’ interpersonal skills. Educators can create an environment that fosters teamwork and encourages […]
[…] to address areas of difficulty. It reduces unnecessary tasks or eliminates repetitive drills; students can focus on meaningful learning experiences. This approach ensures that learning remains engaging and effective, promoting […]